How u will asses T/C performance?
Ans: The main guide to the operating efficiency will be the difference in the gas temperature across the turbine. This is a guide to the amount of energy in the exhaust gas utilized by the turbocharger. If the temperature after the turbine increases then the operating efficiency is falling. The figures obtained can be compared to readings taken after a turbocharger overhaul, when it should be operating at maximum efficiency.
A drop in efficiency on the air side will result in a lower scavenge air pressure for a given turbocharger speed. This is assuming that other causes such as a dirty air filter are not responsible.
Turbocharger surging:
The air pressure generate from the T/C, if gets any restriction or resistance to flow & pass through air cooler. on its way, if back pressure and flow creates which hit back the compressor impeller of the T/C and produce a loud gulp or howling sound which is call surging.
Causes:
1. Any factor which causes change in air mass flow rate.
2. Excess fouling in the system like-
Intake air filter
Compressor or turbine wheel
Turbine blades
Nozzle ring
Exhaust gas economizer
Blockage of air filter.
3. Sudden load change during maneuvering, bad weather & overloading.
4. The changes in engine RPM which causes vibration in the air flow rates.
Fuel starvation, dirty fuel filter and fuel system component defective like fuel pump, injector,high pressure pipe damaged or several wrong timing.
Action:
- Reduced engine speed
- Dirty or fouled component to be checked and cleaned.
- Regular gas and air side washing carried out.
- Proper matching of T/C to the engine.
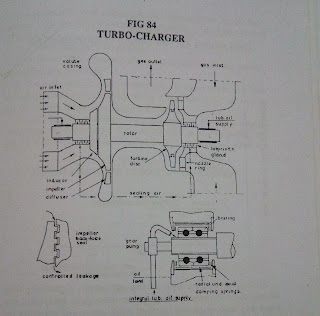 |
| Turbocharger Cross Section |
What is K- value? What is K1 and K2?
Ans: It is a distance between the rotor shaft end & the flange of bearing cover measured at blower side (axial clearance)
Remove the suction cover and measure the critical clearance .It is the distance between the compressor end cover mounting face and shaft end .Mark it as K.
Pull the rotor shaft towards the compressor side until the impeller comes in contact with the insert and determine K2.
Impeller clearance L = K - K2
Thrust the rotor shaft towards the turbine side until the turbine disc and nozzle ring comes in contact with each other and measure K1
Disc clearance M = K1 – K
Procedure for Turbocharger Overhaul
Overhauling is carried out as per planned maintenance of turbochargers. The procedure for overhauling diesel engine turbocharger is explained below.
- Lock off the engine staring mechanism.
- Remove the turbocharger air filter.
- Drain off the oil from both drain plugs.
- Remove the bearing covers from both sides.
- Remove the locking wires.
- Unscrew the hexagon screws and remove oil suction pipes.
- Tighten again the hexagon screws of the bearing boxes.
- Check the deflection of the divergent nozzle by using pick tester and magnet stand.
- Remove the divergent nozzle by screw driver.
- Measure the K value at the blower side by using depth micrometer or caliper and straight edge.
- Lock the rotor with special tool.
- Extract the lubricating disc.
- Extract the both bearings by bearing extractor.
- The various parts should be warped in waxed paper to protect them against dirt and moisture.
- Checks on Turbocharger while Overhauling
- Check the deflection of divergent nozzle.
- Measure the K value at blower side.
- Change the bearing on both sides with the new one (because bearing service life is same as turbocharger overhauling time).
- Clean blower and turbine side with chemical and inspect carefully.
- Check the labyrinth seal.
- Made clear the labyrinth seal air line
- Check the casing for crack & wear
- Blade condition
- After reassembled, check Static Balance
- Check Impeller and Casing clearance
After removing Rotor shaft:
1. Decarbonizes Turbine and Blower blades, and check the blade condition.
2. Check Labyrinth seals.
3. Check bearing c1earances: 0.2 ~ 0.3 mm for Axial, 0.15 ~ 0.2 mm for Radial,
4. Check Nozzle Ring condition.
After refitting Rotor assembly:
1. Push Rotor from Turbine side to Blower side, and measure ‘K1’ at Blower side. [‘L’ = 0, at this time]
2. Push Rotor from Blower side to Turbine side, and measure ‘K2’ at Blower side.[‘M’= 0, at this time]
After adjusting Rotor’s smooth optimum rotation:
1. Secure the locknut (hexagonal screw) of Blower side bearing
2. Measure ‘K’ value at Blower end. [By Dept h Micrometer or Caliper and Straight Edge]
3. Calculate ‘L’ and ‘M’ values. [L=K-K1] and [M=K2 – K] and compare them with actual
values.
How to measure T/C axial and radial clearances:
» Axial Clearance: Push the shaft and measure by Depth Gauge.
» Radial Clearance: Lift the shaft and measure by Dial Gauge.
Purpose of nozzle ring:
- Expand the exhaust gas.
- Direct exhaust gas to turbine blade.
- Convert the pressure energy of gas to kinetic energy giving a high velocity.
Q. Function of labyrinth seals.
Ans:
1. The bearing is separated from the blower & turbine by labyrinth seal.
2. Avoid L.O. leakage inside blower and turbine casing.
2. To prevent contamination of oil by the exhaust gas.
T/C Vibration:
1. Unbalanced.
2. Bearing defects.
3. Deposits in nozzle ring.
4. Impingement.
5. Surging, Scavenge Fire, Overloading.
Function of Diffuser:
1. To direct the air smoothly into Volute Casing.
2. Convert KE to PE of Inlet Air.
Function of Inducer:
» To guide the Air smoothly into the eye of Impeller.
Turbocharger cutting-off procedures:
» When it is necessary to cut-off T/C due to heavy vibration, bearing failure, etc. cutting procedure should be done as per engine maker’s instruction.
» Cutting-off operation depends on number of T/ C installed and number of T/C damaged.
Following procedures are in accordance with Sulzer RT engine practice:
Case I: Failure of one T/C with Exhaust by-pass piping:
1. Lock rotor as per T/C manual.
2. Remove blank flange in by-pass exhaust piping.
3. Open covers of scavenge air trunk.
4. Auxiliary blowers must be running during operation.
5. If casing is cracked, stop T/C cooling.
6. If T/C is supplied with external lubrication, shut L.O. supply. Output 25%: RPM 60% at MCR.
Case II: Failure one T/C. of two T/C engine:
1. Lock rotor of damaged T/C.
2. Remove expansion joints of both exhaust inlet and air outlet of damaged T/C and put blank flanges.
3. If casing is cracked, stop T/C cooling.
4. If T/C is supplied with external lubrication shut L.O. supply. Output 50%: RPM 80%: Running T/C rpm must not exceed normal rpm
Case Ill: Failure of all T/C of an engine, without Exhaust by-pass piping:
1. Lock rotors of all T/Cs.
2. Open all covers of scavenge air trunk.
3. Auxiliary blowers must be running during operation.
4. If casing is cracked, stop T/C cooling.
5. If T/C is supplied with external lubrication shut L.O. supply. Output 15%: RPM 50%:
Cereal Grains or Activated Charcoal Particles Cleaning of Turbine:[Dry Cleaning]
1. Turbine side cleaning is superseded by Coconut Charcoal particles, with grain size of 12 to 34 meshes.
2. No speed reduction required and cleaning can be done at full speed once every 240 hours.
3. Compressed air of (3~5 bars) is used to help the grains strike the deposited Turbine Blades and Nozzles, giving effective cleaning of hard particles.
4. Air supply pipe is fitted to solid grain container, and grains are injected into Exhaust System by air pressure, at the same point (as in Water washing) just after Exhaust Grids.
5. Turbine casing drain kept open during cleaning time of (about 2 minutes only), until drains become clear.
Advantages of Solid Cleaning:
1. No reduction in RPM, thus no effect on scheduled voyage.
2. No water required, thus no corrosion and thermal stresses.
3. Cleaning time, shortened to about 2 minutes only.
4. Charcoal does not wear down the Turbine Blades.
5. Combustion residues and bard particles, effectively removed.
Difference between Mitsubishi and Man T/C.
Mitsubishi t/c is pulse type and man t/c r constant pressure type.
How to calculate t/c efficiency?
How will you carry out turbocharger turbine and blower side water washing ?
- Blower side water washing
- It can be done when M/E on full load.
- Fill up the warm fresh water to hopper and closed the cover.
- Open the valve and water will flow into the blower casing and mechanically attack the blower blades and clean the deposit.
- Close the valve, open the cover and check the cleaning water must be empty.
Turbine side water washing procedure
- Turbine side water washing can be made with hot fresh water.
- Inform to the bridge
- Reduce the M/E rpm to recommended speed and hence turbocharger rpm.
- Check the water washing injection nozzle if fitted. (directly aim to the exhaust grips before entering to the turbocharger)
- Open turbocharger drain valve.
- Open the water supply about 1 bar to turbine side.
- Water washing must be made until the clean water comes out.
- Close the water supply and remove the nozzle.
- Exhaust side drain can be closed after all water is drained out and dried.
- Inform to the bridge and increase the M/E rpm gradually to sea speed.
- The turbine side water washing is usually at departure after manoeuvring time.
- For usual practice cleaning is done at every 500 hr, running hour depending on the cleanliness of the turbocharger .
Grit Washing or Dry Cleaning of Turbocharger
- Turbine side cleaning is superseded by walnut shell, with grain size of 12 to 34 mesh.
- No speed reduction required and cleaning can be done at full speed, once every day
- Compressed air of (3 -5 bar) is used to help the grains strike the deposited Turbine Blades and Nozzles, giving effective cleaning of hard particles
- Air supply pipe is fitted to solid grain container, and grains are injected into exhaust system by air pressure, at the same point (as in water washing ) just after exhaust grids
- Turbine casing drain kept open during cleaning time (about 2 minutes only)
What measurements are taken during auxiliary engine turbocharger overhaul ?
How to measure turbocharger axial and radial clearance ?
Difference between constant and pulse turbocharger?
Advantages and Disadvantages for Constant Pressure System
Advantages
- Good performance in high load (Efficient when Bmep is above 8 bar)
- More suitable for high output engine.
- There is no need to group the cylinders exhaust into multiple of three. (Simple piping system)
- No exhaust grouping
- High turbine efficiency due to steady flow of exhaust.
- The work transfer at the turbine wheel is smooth.
- Reduction in SFOC (Specific Fuel Oil Consumption) of 5% – 7%
Disadvantages
- When running at reduced speed and starting up low available energy at turbine. Thus it supplies inadequately air quantity of the scavenge pressure necessary for efficient scavenging and combustion.
- It require scavenge assistant (Auxiliary Blowers).
- Poor response in changing load.
Pulse System
- Makes full use of the higher pressure and temperature of the exhaust gas during the blow down period
- While rapidly opening the exhaust valves, exhaust gas leave the cylinder at high velocity as pressure energy is converted into kinetic energy to create the pressure wave or pulse in exhaust
- These pressure waves or pulses are lead directly to the turbocharger
- Exhaust pipe, so constructed in small diameter, is quickly pressurized and boosted up to form pressure pulse or wave
- Pressure waves reach to turbine nozzles and further expansion takes place.
Turbocharger Arrangement in Pulse System
- Interference exists between exhausting and scavenging among cylinders
- To prevent this, cylinders are grouped relatively with connections to two or more exhaust pipes
- Pipes are arranged, in small diameter to boost up pressure pulse and in short, straight length to prevent energy loss
- Number of exhaust branch depends upon firing order, number of cylinders and turbocharger design
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pulse System
Advantages
- At low load and low speed it is more efficient (Still efficient when Bmep is < 8 bar)
- No need assistant of scavenge pump and blower at any load change.
- It is highly response to change engine condition giving good performance of all speed of engines.
- High available energy at turbine
- Good turbocharger acceleration
Disadvantages
- The exhaust grouping is complicated.
- Different sizes of exhaust pipes are needed for spare.
- High pressure exhaust from one cylinder would pass back into another cylinder during the low pressure scavenging period thus adversely effecting the combustion efficiency.
How to Overhaul and Repair a Marine Turbocharger
Introduction
Safety while Dismantling the Turbocharger
- Inform the operating personnel accordingly before starting any maintenance work on turbocharger.
- As a precaution, place a receptacle for leaking oil under the turbocharger.
- Before starting work, secure the rotor against turning.
- Ensure that absorbent material is available to soak up any spilled oil.
- Ensure that operation and process materials are drained, collected, and disposed of in a safe manner.
- Ensure that all spares and tools are available for dismantling and assembling.
- Dismantled safety devices must be reassembled and subjected to a functional test immediately after conclusion of maintenance and repair.
Tools Required for Dismantling
- Open and ring spanner
- Box spanner
- Claw spanner
- Tommy spanner
- Bearing pushing tool
- Bearing pulling tool
- Pump disc locking plate
- Pump removing tool set (provided by manufacturer)
- Impeller removing tool set (provided by manufacturer )
- Shaft pushing tool
- Clearance measuring instruments
- Screw driver
Preliminaries before Dismantling:
- Before dismantling, exhaust gas from the turbine should be bypassed and a blanking plate should be fitted in turbine inlet casing.
- Drain the lube oil from the built-in sump.
- Remove the turbine side cooling water connection and drain all water

excellent
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteI am very impressed with your post because this post is very beneficial for me and provide a new knowledge to me
Output Thermal VST Crack